Featured
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Central Limit Theorem Statistics Definition
Central Limit Theorem Statistics Definition. The significance of the central limit theorem lies in the fact that it permits us to use sample statistics to make inferences about population parameters without knowing anything about the shape of the frequency distribution of that population other than. Saul mcleod, published nov 25, 2019.
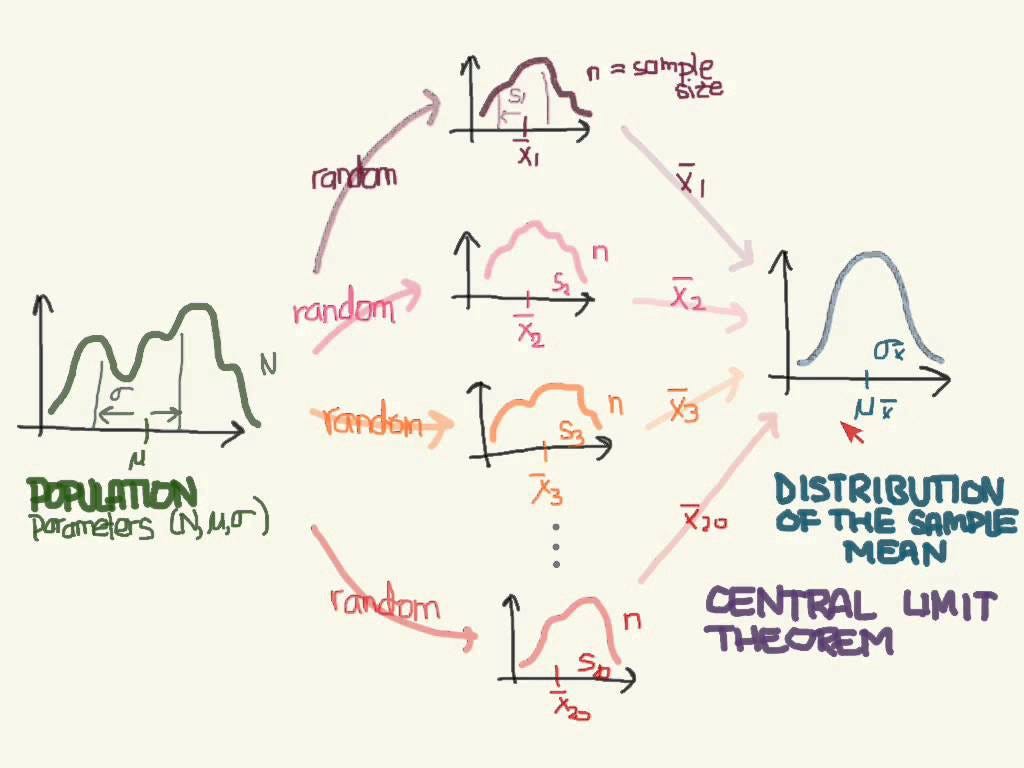
The significance of the central limit theorem lies in the fact that it permits us to use sample statistics to make inferences about population parameters without knowing anything about the shape of the frequency distribution of that population other than. An essential component of the central limit theorem is that the average of your sample means will be the population mean. The central limit theorem and the law of large numbers are related in that the law of large numbers states.
In Other Words, The Central Limit Theorem States That For Any Population With Mean And Standard.
The central limit theorem states that if you have a population with mean μ and standard deviation σ and take sufficiently large random samples from the population with replacement, then the distribution of the sample means. Population is all elements in a group. Central limit theorem can also be defined in terms of the calculus limit.
Moving On, The Standard Definition:
Plausibly, add the averages of all of your samples together and calculate the average, which the population means. The central limit theorem and means. If lim n!1 m xn (t) = m x(t) then the distribution function (cdf) of x nconverges to the distribution function of xas.
The Central Limit Theorem States That Irrespective Of A Random Variable's Distribution If Large Enough Samples Are Drawn From The Population Then The Sampling Distribution Of The Mean For That Random Variable Will Approximate A Normal Distribution.
One which is much applied in sampling and which states that the distribution of a mean of a. The central limit theorem (clt) is a fundamental and widely used theorem in the field of statistics. The central limit theorem states that whatever the distribution of the sample mean is there, approximates normal distribution as the sample size gets larger anyhow of the population distribution
Central Limit Theorem (Clt) States That Given A Sufficiently Large Sample Size, The Sampling Distribution Of The Mean Of A Variable Will Approximate A Normal Distribution Regardless Of That Variable’s Distribution In.
Definition of central limit theorem. Let x nbe a random variable with moment generating function m xn (t) and xbe a random variable with moment generating function m x(t). Definition + examples the central limit theorem states that the sampling distribution of a sample mean is approximately normal if the sample size is large enough, even if the population distribution is not normal.
This Fact Holds Especially True For Sample Sizes Over 30.
What is central limit theorem in statistics? Saul mcleod, published nov 25, 2019. The significance of the central limit theorem lies in the fact that it permits us to use sample statistics to make inferences about population parameters without knowing anything about the shape of the frequency distribution of that population other than.
Comments
Post a Comment